The Julian calendar, introduced by Julius Caesar in 46 BC, was the predominant calendar in the Western world for over 1,600 years. It was based on a 365-day year with an extra day added every four years to account for the Earth’s orbit around the sun.
However, the Julian calendar had a slight miscalculation in the length of the solar year, leading to a discrepancy with the actual solar year. This discrepancy eventually led to the adoption of the Gregorian calendar in most countries.
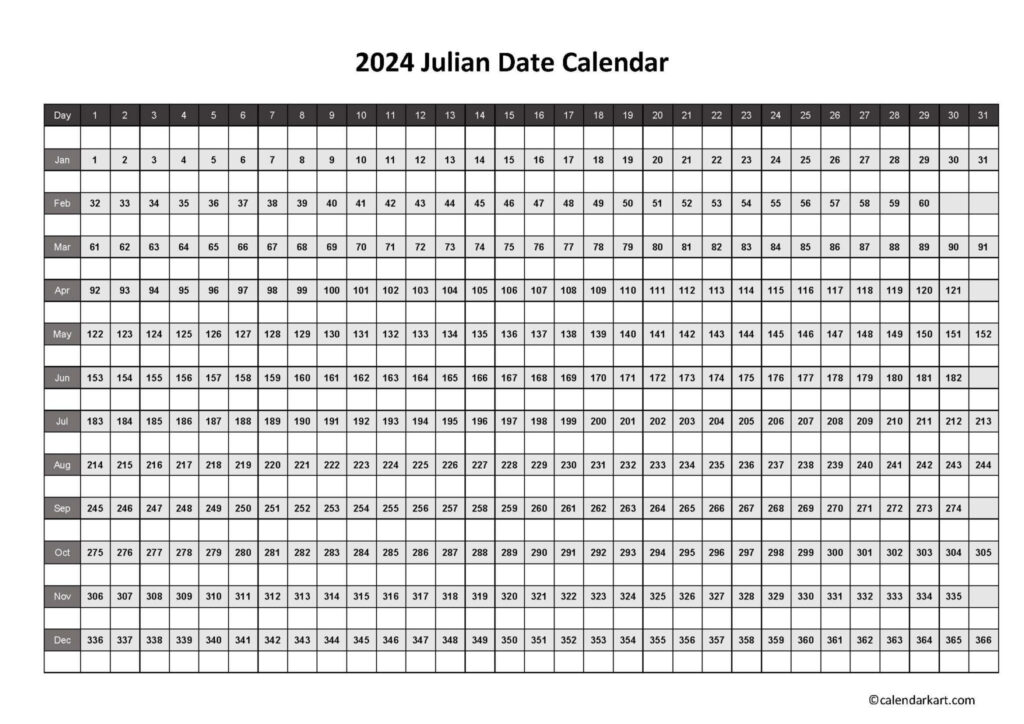
Today In Julian Calendar
How to Calculate Today in Julian Calendar?
To calculate today’s date in the Julian calendar, you would need to adjust for the difference between the Julian and Gregorian calendars. The Julian calendar is currently 13 days behind the Gregorian calendar, so you would need to subtract 13 days from the current date in the Gregorian calendar to find the corresponding date in the Julian calendar.
For example, if today is October 1st in the Gregorian calendar, the corresponding date in the Julian calendar would be September 18th. This adjustment is necessary when converting dates between the two calendar systems.
Why is the Julian Calendar Still Relevant Today?
While the Julian calendar is no longer used as the primary calendar system in most countries, it is still relevant in certain contexts. For example, some Orthodox churches still use the Julian calendar to calculate religious holidays such as Easter.
Additionally, historians and astronomers may use the Julian calendar to reference historical events or astronomical data that was recorded using the Julian calendar system. Understanding the Julian calendar can provide valuable insights into the history of timekeeping and the evolution of calendar systems.