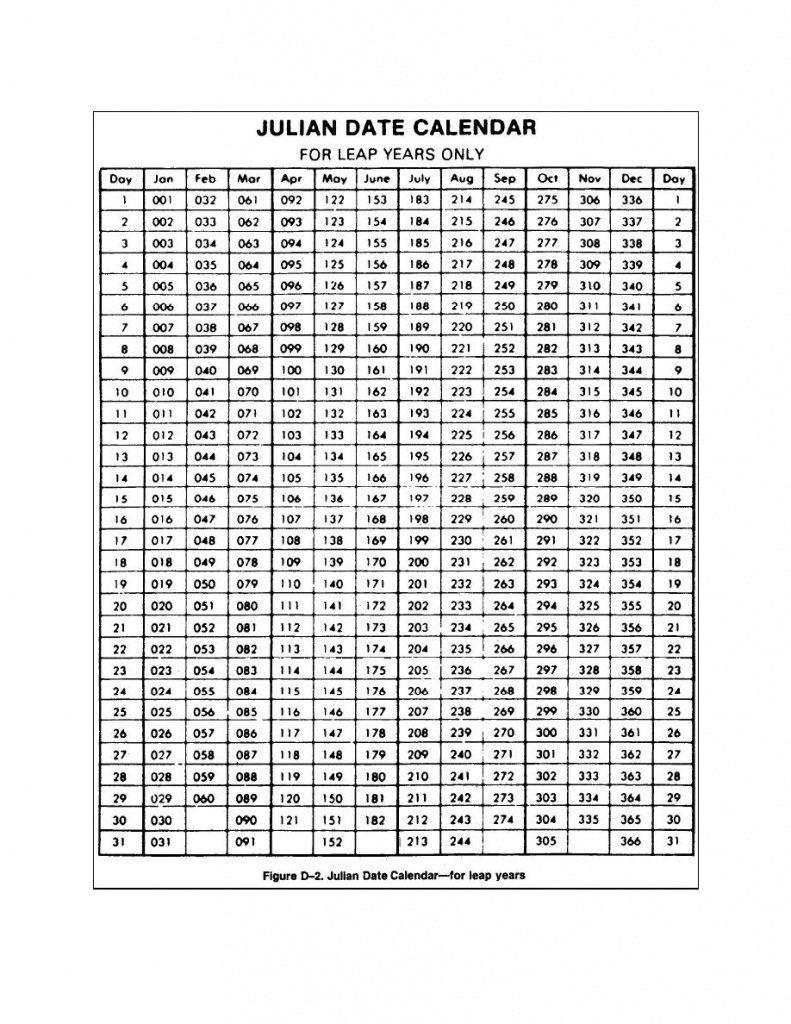
The Julian calendar is a calendar system introduced by Julius Caesar in 46 BC. It was used as the predominant calendar in most of Europe for more than 1600 years until it was replaced by the Gregorian calendar in 1582. The Julian calendar was based on a 365-day year, with an extra day added every four years to account for leap years.
The Julian calendar was named after Julius Caesar, who implemented it as a reform of the Roman calendar. It was designed to align the calendar year with the solar year, which is approximately 365.25 days long. This made the Julian calendar more accurate than previous calendar systems, which often had inconsistencies in their reckoning of leap years.
Date In Julian Calendar
How to Calculate a Date in Julian Calendar?
To calculate a date in the Julian calendar, you need to know the number of days that have elapsed since the starting point of the calendar system. The Julian calendar starts on January 1, 4713 BC (Julian calendar) and counts days continuously from that point onwards.
To convert a Gregorian date to a Julian date, you can use a simple formula: Julian Day = (1461 * (Year + 4800 + (Month – 14)/12))/4 + (367 * (Month – 2 – 12 * ((Month – 14)/12)))/12 – (3 * ((Year + 4900 + (Month – 14)/12)/100))/4 + Day – 32075.
By using this formula, you can accurately calculate the Julian date for any given Gregorian date. This can be useful for historical research, astronomy, or other applications where the Julian calendar is still relevant.